Contents
The Duo OIDC Auth API is an OIDC standards-based API for adding strong two-factor authentication to your web application. This API supports the Duo Universal Prompt, which uses a new OIDC-compliant authentication protocol to perform two-factor authentication.
If you need a solution that performs both primary and secondary authentication flows for OIDC applications, try Duo Single Sign-On for Generic OIDC Relying Parties.
Overview
Duo uses the OpenID Connect protocol to deliver two-factor authentication to users and make available the result of the two-factor authentication. The flow begins with a health check to Duo's service, followed by a request for authorization. After validating this request, Duo redirects the user to a Duo-hosted site for multi-factor authentication. Upon a successful second-factor authentication Duo redirects the user to the redirect URI supplied in the initial Authorization request. To retrieve the result of the second factor authentication from Duo the client will make a request to the Access Token endpoint. The response includes contextual information about the Duo authentication event.
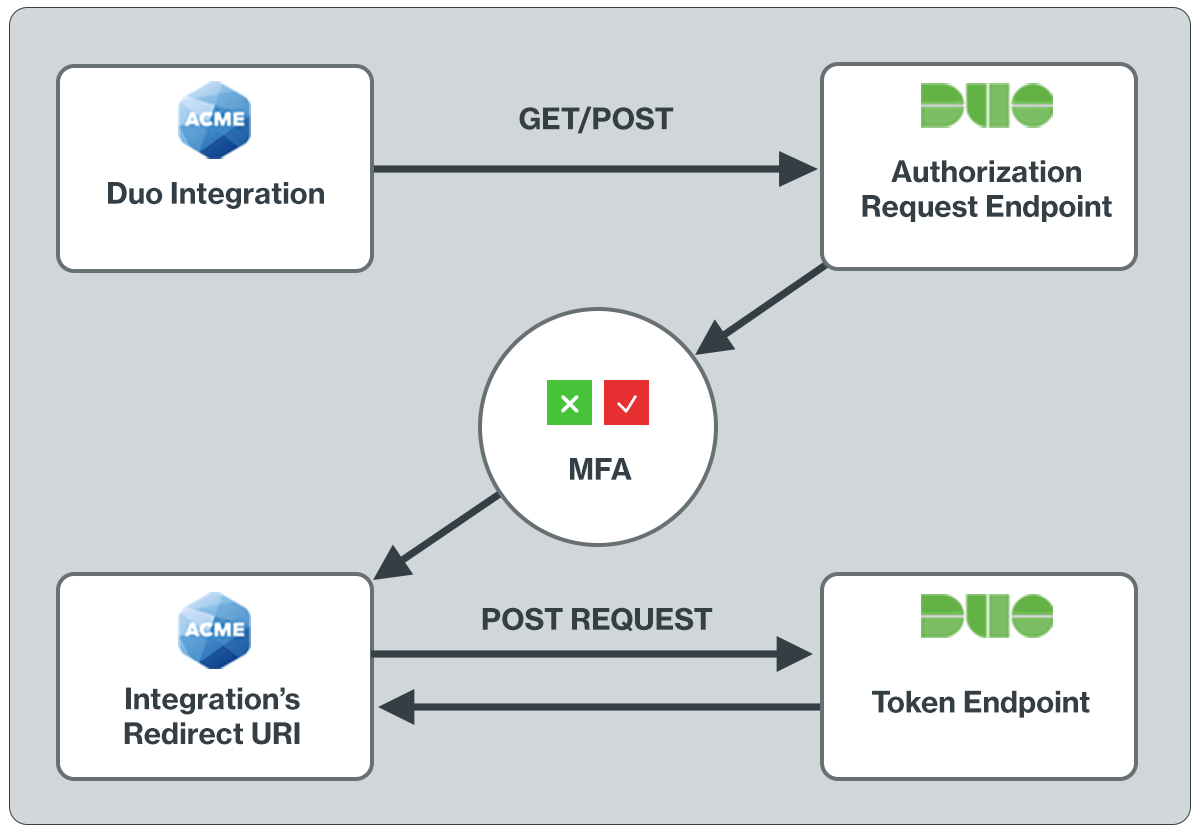
The redirect URI is a critical part of adding support for the Duo Universal Prompt. After a successful two-factor authentication, the end-user must be sent to a page which will retrieve the result of the authentication. The redirect URI parameter in the JWT sent to Duo in the first authorization request tells Duo where to redirect the end-user. Duo’s use of an explicit authorization code flow for the OIDC spec sufficiently protects against attacks which redirect requests to URIs controlled by bad actors.
You may not load the OIDC-based Duo prompt in an iFrame on your site. The redirect to Duo to show the prompt and back is required.
The client can configure their desired behavior in the event of a failed health check to determine whether a user should be granted access to their protected resources or prevented from doing so.
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are used in each request and should be signed using the secret key you are provided when protecting an application.
NOTE: Adding Duo using the OIDC API requires custom development and some understanding of your application's language and authentication process.
To add Duo to your application using our client SDKs for Python, Java, Go, NodeJS, PHP, or C#, see the Duo Web SDK v4 instructions.
Unsupported OIDC Endpoints
Duo’s implementation of OIDC for two-factor authentication does not require and therefore does not support the following endpoints/code flows:
- UserInfo - Required for Primary.
- Discovery Endpoint - Required for Primary.
- Refresh - By design 2FA token should be valid only once.
- JWKS - Duo does not currently support asymmetric signing and thus does not have an endpoint to describe public keys and their rotations.
First Steps
To begin development with a new Duo Web SDK integration:
- Sign up for a Duo account.
- Log in to the Duo Admin Panel and navigate to Applications.
-
Click Protect an Application and locate the 2FA-only entry for Web SDK in the applications list. Click Protect to the far-right to configure the application and get your Client ID, Client secret, and API hostname. You'll need this information to complete your setup. See Protecting Applications for more information about protecting applications in Duo and additional application options.
Previously, the Client ID was called the "Integration key" and the Client secret was called the "Secret key".
- Use NTP to ensure that your server's time is correct.
Documented properties will not be removed within a stable version of the API. Once a given API endpoint is documented to return a given property, a property with that name will always appear (although certain properties may only appear under certain conditions).
New, undocumented properties may also appear at any time. For instance, Duo may make available a beta feature involving extra information returned by an API endpoint. Until the property is documented here its format may change or it may even be entirely removed from our API.
Universal Prompt
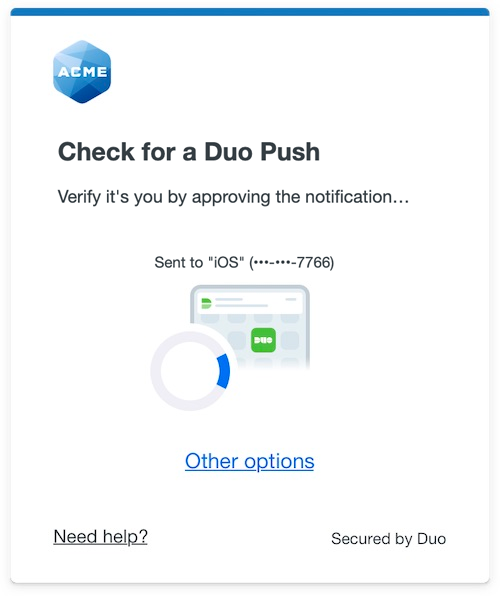
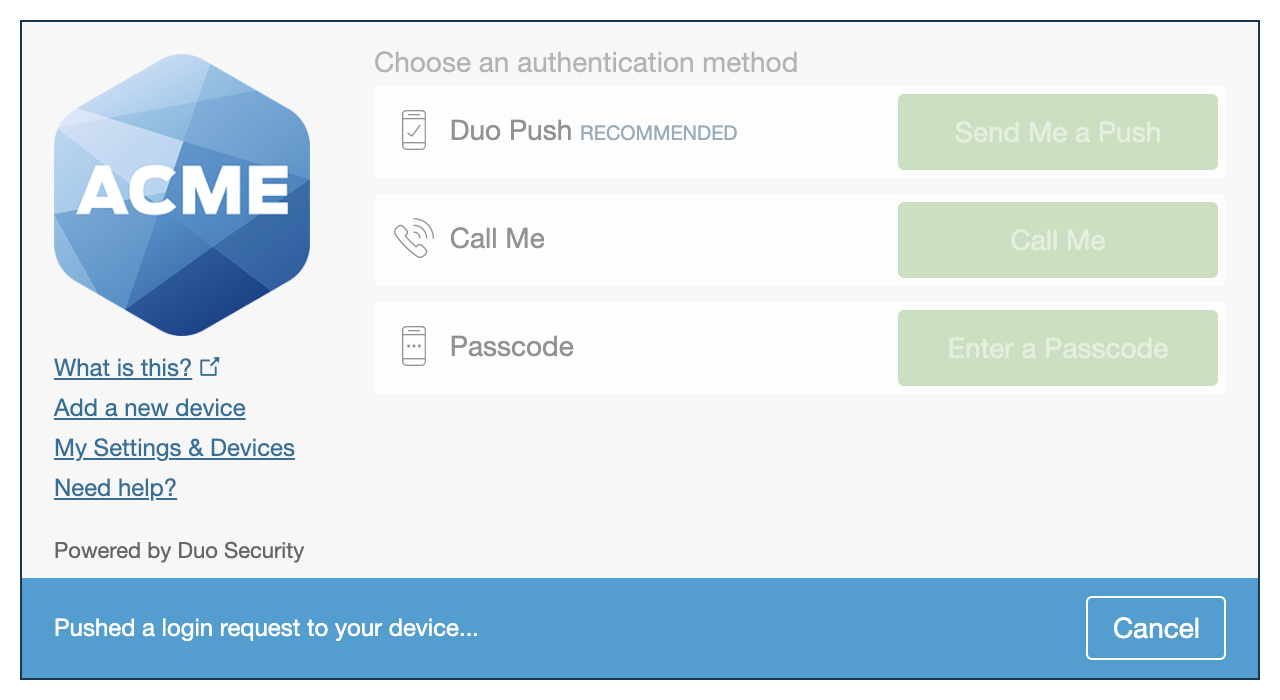
The Duo Universal Prompt provides a simplified and accessible Duo login experience for web-based applications, offering a redesigned visual interface with security and usability enhancements.
| Universal Prompt | Traditional Prompt |
 |
 |
Migration to Universal Prompt for your Duo Web application is a two-step process:
- Build your application with support for the Universal Prompt by using the OIDC Auth API.
- Activate the Universal Prompt experience for users of that Duo Web application.
If you're creating a Duo Web application for the first time, building it with the OIDC Auth API or Duo Web v4 SDK ensures it supports the Universal Prompt.
Duo Prompt UI Support per Delivery Method
| OIDC Redirect (Web SDK v4) | Iframe (Web SDK v2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Universal Prompt | YES | NO |
| Traditional Prompt | YES | YES |
New Web SDK Applications
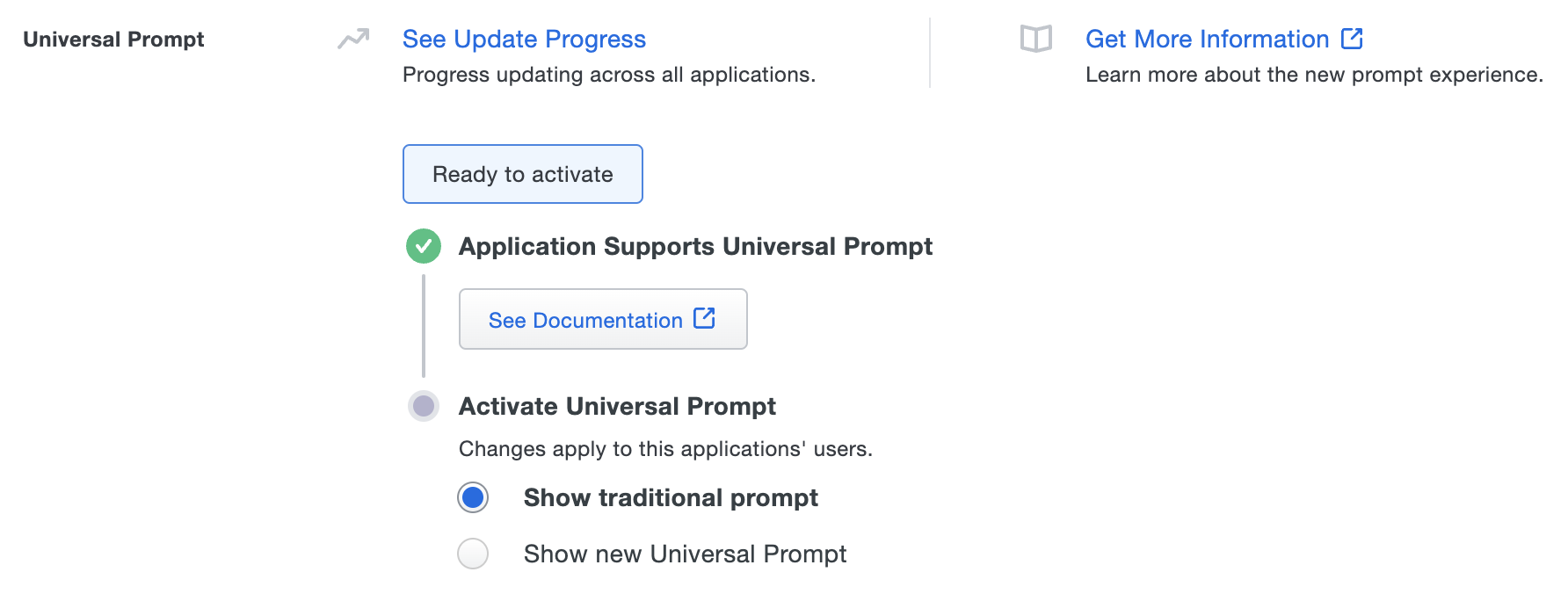
The "Universal Prompt" section on the details page of your new Duo Web SDK application shows the status as "Ready to activate", with these activation control options:
-
Show traditional prompt: (Default) Your users experience Duo's traditional prompt when logging in to this application.
-
Show new Universal Prompt: Your users experience the Universal Prompt when logging in to this application.
Existing Web SDK Applications
The "Universal Prompt" section on the details page of your existing Duo Web v2 iframe application will show the status as "Updated required" with a link to update instructions if an application software update is available.
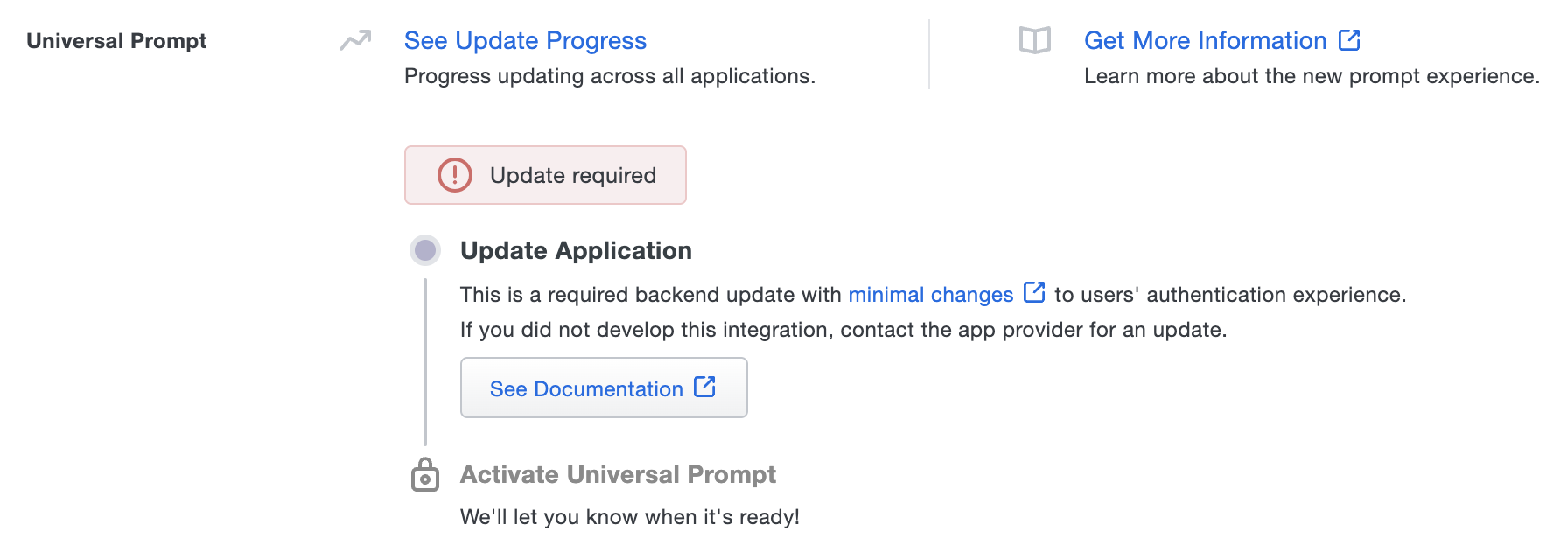
Once you update your Duo integration to use OIDC Auth API or Web SDK v4, and a user authenticates to that existing application via the frameless OIDC-based prompt, the "Universal Prompt" section of the Duo Web application page reflects a status change to "Ready to activate", with these activation control options:
-
Show traditional prompt: (Default) Your users experience Duo's traditional prompt when logging in to this application.
-
Show new Universal Prompt: Your users experience the Universal Prompt when logging in to this application.

In addition, the "Integration key" and "Secret key" property labels for the application update to "Client ID" and "Client secret" respectively. The values for these properties remain the same.
Activate Universal Prompt
Activation of the Universal Prompt is a per-application change. Activating it for one application does not change the login experience for your other Duo applications.
Enable the Universal Prompt experience by selecting Show new Universal Prompt, and then scrolling to the bottom of the page to click Save.
Once you activate the Universal Prompt, the application's Universal Prompt status shows "Activation Complete" here and on the Universal Prompt Update Progress report.
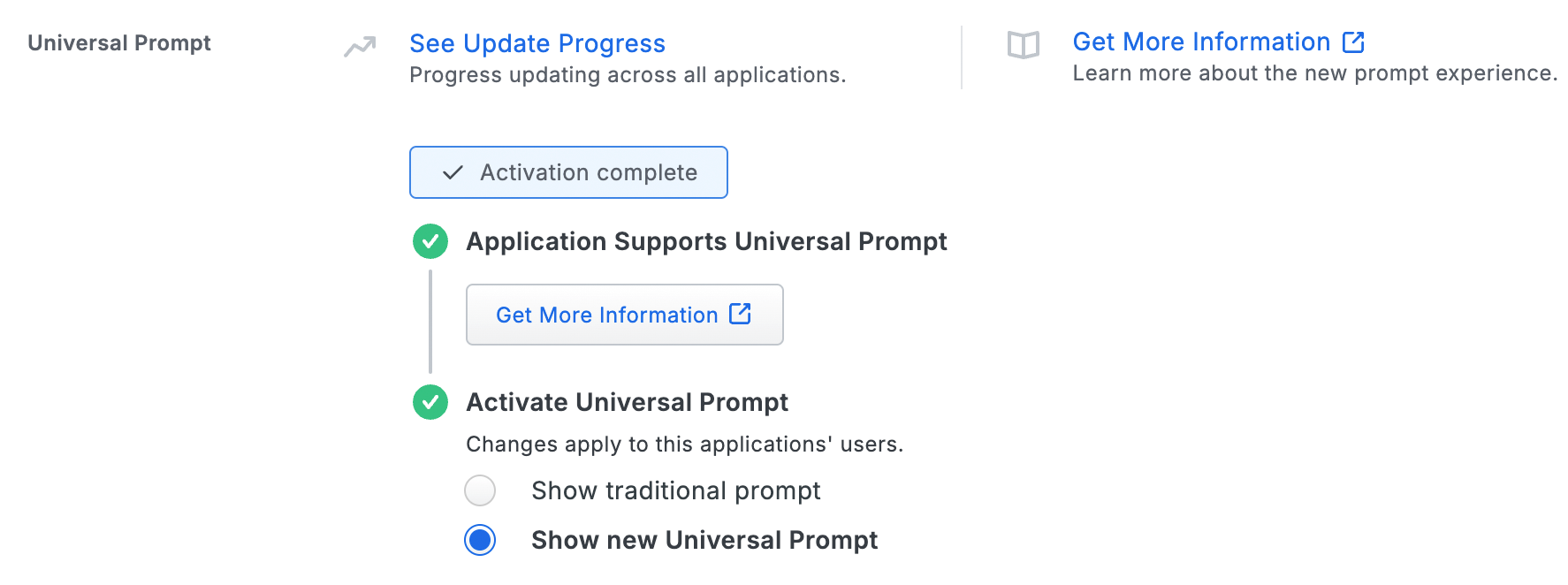
Should you ever want to roll back to the traditional prompt, you can return to this setting and change it back to Show traditional prompt.
Universal Update Progress
Click the See Update Progress link to view the Universal Prompt Update Progress report. This report shows the update availability and migration progress for all your Duo applications that will have Universal Prompt support. You can also activate the new prompt experience for multiple supported applications from the report page instead of visiting the individual details pages for each application.
Watch the Duo Blog for future updates about the Duo Universal Prompt.
JSON Web Tokens
JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) are the secure mechanism with which Duo will verify that the request is coming from a trusted client application. More information about the structure of JWTs can be found at JWT.IO and RFC 7519.
JWTs are encoded as a single string, but when decoded have three sections: the header, the payload, and the signature.
Example of an encoded JWT

Example of the encoded JWT above decoded and separated into each section
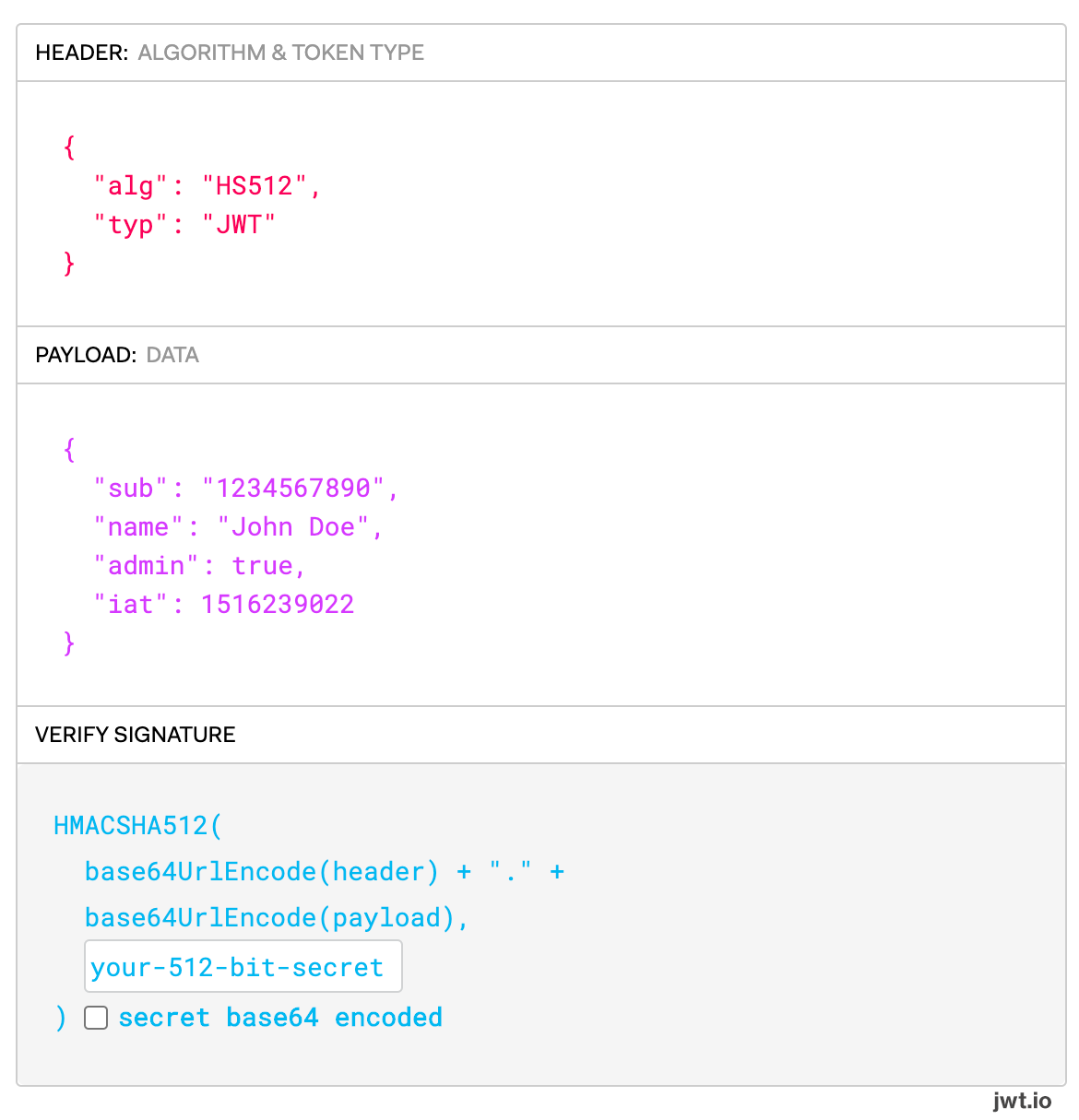
In the header, Duo requires that the typ field is equal to JWT and that the alg field is either HS256 (HMAC using SHA-256) or HS512 (HMAC using SHA-512). We also require use of the HS256 or HS512 HMAC algorithms to sign the request.
The signature for each JWT should use the client secret value (also shown as the "secret key" depending on when you created your Duo Web SDK application) that you can find on your integration’s page in the Admin Panel.
For each OIDC endpoint there exists a required field for supplying a JWT. Each JWT will have the same requirements for the header and signature, but the payload data shape has differing format described as the field name followed by .payload in the endpoint details below. For example, in the Health Check endpoint /oauth/v1/health_check we require that a client_assertion parameter is provided with a value of type JWT. We denote the shape of that JWT payload with the parameter name of client_assertion.payload.
Please note that all Unix timestamps are in seconds.
Endpoints
Health Check
To ensure that all Duo services are operating we require a call to a health check endpoint with arguments that enable us to verify your integration is properly configured.
POST/oauth/v1/health_checkArguments
| Argument | Type | Required? | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
client_id
|
String | Required | This value was previously referred to as the integration key. Locate the value on the application's page in the Duo Admin Panel. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
client_assertion
|
JWT | Required |
See below for the expected client_assertion payload.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
client_assertion.payload
|
Object | Required |
|
Example Response
Success:
{
"stat": "OK",
"response": {
"timestamp": {int32} The time at which the health check occurred.
}
}Failure:
{
"stat": "FAIL",
"code": {String} An API error code which corresponds to our existing API error documentation,
"timestamp": {int32} The time at which the health check occurred,
"message": {String} The failure error message,
"message_detail": {String} Additional information about the error.
}Authorization Request
This endpoint processes your application’s request for Duo to perform multi-factor authentication and sends the end-user to the Duo-hosted multi-factor authentication prompt. We require various fields to be sent in a JWT with this request in order to determine the validity of the request.
After Duo processes this request, this endpoint will return a response that redirects the end user to a Duo hosted domain to perform multi-factor authentication. This is the same domain that was previously used as the source of the iframe that delivered the authentication prompt.
In the event that multi-factor authentication is unsuccessful, we will not redirect the end-user to the specified redirect URI. A failed authentication will appear in the Authentication Log (found in the Admin Panel) associated with the end-user.
After a successful authentication, Duo redirects the user to the redirect URI specified in the redirect_uri field as described below.
GET/oauth/v1/authorizePOST/oauth/v1/authorizeGET and POST requests require the same parameters and have the same expected response.
Arguments
| Argument | Type | Required? | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
response_type
|
String | Required |
We expect the value code to be present for this field.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
client_id
|
String | Required | This value was previously referred to as the integration key. Locate the value on the application's page in the Duo Admin Panel. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
request
|
JWT | Required | See below for the expected request payload. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
redirect_uri
|
String | Optional | The URI where the end-user will be redirected after a successful auth. While supplying this value in the query parameters is optional, if provided it should match the value provided in the JWT payload. Must be well-formed with a valid HTTPS URL and port, using an RFC-compliant hostname. Maximum length: 1024 characters. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
scope
|
String | Optional |
The scope must be openid. A different value or multiple values will fail.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
nonce
|
String | Optional | If provided, this must be a random value that is cryptographically secure such that it is unguessable by a third party. We require a length of at least 16 characters and at most 1024 characters. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
state
|
String | Optional | A random, cryptographically secure value that the client must maintain throughout the authentication. We require a length of at least 16 characters and at most 1024 characters. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
request.payload
|
Object | Required |
|
We require that the state parameter be sent in either the JWT payload OR in the request query parameters. If the state parameter is present both in the JWT payload and in the request query parameters, we will honor the value sent in the request query parameters. Additionally, while the nonce parameter is optional, if it is sent in both the JWT payload AND the request query parameters, we will honor the value sent in the request query parameters.
Access Token
The success response to the redirect URI sent previously will have the following structure:
{
code {String}: A randomly generated authorization code that will be used to retrieve
the result of the authentication,
state {String}: This should be the value for state passed in to the original request.
It is up to the client to verify that it is the same value as a security
measure. This value specifically protects against CSRF attacks (see RFC 6749).
}This code can then be exchanged for an ID Token that includes contextual information about the two-factor authentication via a POST request to the Token Endpoint.
If the custom claim of use_duo_code_attribute was sent with a value of true in the authorization request JWT, then the authorization code parameter name will be duo_code instead of code.
POST/oauth/v1/tokenArguments
| Argument | Type | Required? | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
grant_type
|
String | Required |
This must be equal to the string authorization_code.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
code
|
String | Required |
This must be equal to the string code received in the previous response.
|
redirect_uri
|
String | Required |
This must be equal to the redirect URI sent in the request to the Authorization Request endpoint /oauth/v1/authorize.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
client_assertion_type
|
String | Required |
This must be equal to the string value urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer,
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
client_assertion
|
JWT | Required | See below for the required payload fields. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
client_id
|
String | Optional | The Client ID (or Integration key) from the application's page in the Duo Admin Panel. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
client_assertion.payload
|
Object | Required |
|
The response from the Token Endpoint includes an ID token, an access token, and contextual information about the authentication. The access token can not be exchanged for further access because Duo is not a first-factor identity provider.
Response Format
The response follows the structure below:
{
id_token {JWT}: See below for id_token payload structure,
access_token {String}: A random and unique identifier for the authentication session,
expires_in {integer}: The time at which the access token is considered to be expired,
token_type {String}: This will be equal to the string "Bearer".
}
id_token.payload
|
Object |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
auth_result
|
Object |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
auth_context
|
Object | Please see the Duo Authentication Logs reason values for the full authentication log information. |
Duo highly recommends that you perform the ID Token validation steps outlined in the OIDC Specification. Additionally, if your implementation maintains stateful information about the user authenticating you should validate that the user described in the ID token matches your expected user. For example, if you have stored stateful information with the state parameter that user jdoe is authenticating, you should verify that the ID Token specifically has the username jdoe in the preferred_username field.
Example Response
Note that the information returned in the response may vary depending on the Duo edition used and effective policies for the authentication. This example is from Duo Premier edition.
{
"aud": "DI0P00LD4DX50O2VCAVK",
"auth_context": {
"access_device": {
"browser": "Chrome",
"browser_version": "128.0.6613.120",
"epkey": "EP2ULFE874LMXBYJZE4D",
"flash_version": "uninstalled",
"hostname": null,
"ip": "12.106.124.163",
"is_encryption_enabled": true,
"is_firewall_enabled": true,
"is_password_set": true,
"java_version": "uninstalled",
"location": {
"city": "Detroit",
"country": "United States",
"state": "Michigan"
},
"os": "Mac OS X",
"os_version": "14.6.1",
"security_agents": [
{
"security_agent": "cisco-amp",
"version": "1.24.0.967"
}
]
},
"adaptive_trust_assessments": {
"more_secure_auth": {
"detected_attack_detectors": [
"NOVEL_ASN"
],
"features_version": "3.0",
"model_version": "2022.07.19.001",
"policy_enabled": false,
"preview_mode_enabled": true,
"reason": "Low level of trust; detection of one or more known attack patterns",
"trust_level": "LOW"
},
"remember_me": {
"features_version": "3.0",
"model_version": "2022.07.19.001",
"policy_enabled": false,
"reason": "Novel Access IP",
"trust_level": "LOW"
}
},
"alias": "",
"application": {
"key": "DI0P00LD4DX50O2VCAVK",
"name": "Acme Corp"
},
"auth_device": {
"ip": "12.106.124.163",
"key": "DP5IWE1PCVP00LD4D64A",
"location": {
"city": "Detroit",
"country": "United States",
"state": "Michigan"
},
"name": "Norben's Phone"
},
"email": "narroway@example.com",
"event_type": "authentication",
"factor": "duo_push",
"isotimestamp": "2024-09-10T18:57:44.444611+00:00",
"ood_software": null,
"rbfs_triggered_attacks": [
{
"country_code_access": null,
"country_code_auth": null,
"detected_occurrences": 1,
"detector": "NOVEL_ASN",
"shadow_mode": false,
"suppressed": null,
"threshold_occurrences": 1,
"threshold_time_frame": null,
"unrealistic_travel_velocity": null
}
],
"reason": "user_approved",
"result": "success",
"timestamp": 1725994664,
"trusted_endpoint_status": "unknown",
"txid": "08bfd78a-7b70-4818-af15-104744ab3609",
"user": {
"groups": [],
"key": "DU53P00LD4D4C075WQGK",
"name": "narroway"
}
},
"auth_result": {
"result": "allow",
"status": "allow",
"status_msg": "Login Successful"
},
"auth_time": 1725994664,
"exp": 1725998264,
"iat": 1725994667,
"iss": "https://api-nnnnnnnn.duosecurity.com/oauth/v1/token",
"preferred_username": "narroway",
"sub": "narroway"
}Troubleshooting
Need some help? Take a look at our OIDC Auth API Knowledge Base articles or Community discussions. For further assistance, contact Support.
