Contents
Certificate-based Trusted Endpoint verification will reach end-of-life on October 7, 2024. Migrate existing management integrations to solutions that verify endpoint status with Duo Mobile or Duo Desktop. Learn more about migration options in the Duo Trusted Endpoints Certificate Migration Guide.
Overview
Duo's Trusted Endpoints feature lets you define and manage trusted endpoints and grant secure access to your organization's applications with policies that verify systems using device certificates, application verification, or management status.
Duo helps you distinguish between unmanaged endpoints and managed endpoints that access your browser-based applications. The Trusted Endpoints policy tracks whether clients accessing the applications can be identified as managed, or can block access to various applications from systems that aren't managed.
Trusted Endpoints is part of the Duo Essentials, Duo Advantage, and Duo Premier plans.
Duo Desktop Verification
During authentication to a browser-based application that shows Duo's inline, interactive Universal Prompt or traditional Duo Prompt from a Windows, macOS, or Linux device, Duo Desktop installed on the endpoint reports unique device information back to Duo, including machine identifiers. Trusted Endpoints management integrations that use Duo Desktop for verification match the information reported by Duo Desktop to information reported by the endpoint management system to determine the computer's management status.
Duo Mobile Verification
During authentication to a Duo-protected application from an Android or iOS access device, Duo checks for the presence of Duo Mobile, activated for Duo Push authentication, on the device to determine the endpoint's management status.
Certificate Verification
Certificate-based Trusted Endpoint verification will reach end-of-life on October 7, 2024. Migrate existing management integrations to solutions that verify endpoint status with Duo Mobile or Duo Desktop. Learn more about migration options in the Duo Trusted Endpoints Certificate Migration Guide.
During authentication to a browser-based application, Duo checks for a device certificate on the endpoint:
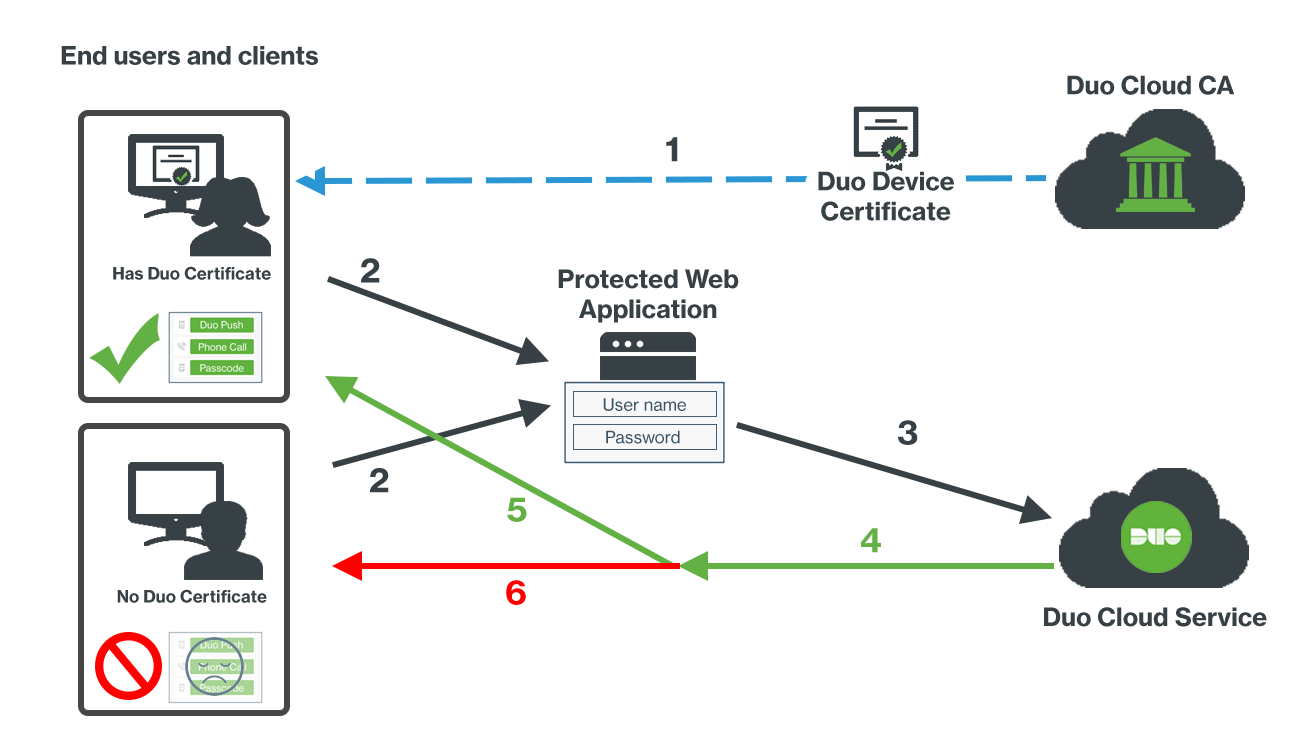
- Duo issues certificates for client authentication to your managed endpoints from our cloud-based public key infrastructure (PKI).
- A user logs into a browser-based, Duo-protected application that shows the inline, interactive Universal Prompt or traditional Duo Prompt.
- Successful primary login to the web application redirects the client to Duo.
- Duo's cloud service applies the Trusted Endpoints policy setting to the access attempt.
- The Duo prompt checks for the Duo device certificate in the user's personal store. If present. Duo reports the endpoint as trusted.
- If the Duo certificate isn't present we report that the endpoint does not have a certificate (and is therefore not a managed endpoint). Application access may be blocked from that device.
Note that the Duo device certificate is not intended for use as a substitute for successful primary authentication to your protected service or application! This is poor security practice and should not be done under any circumstances.
Best Practices for Implementing Trusted Endpoints
Most organizations perform a staged deployment of Duo's Trusted Endpoints policy. Beginning to end, your rollout should proceed like this:
- Identify an application for testing. Applications must use Duo's inline, interactive Universal Prompt or traditional Duo Prompt to report managed/unmanaged status.
- Identify (or create) a Duo group containing your pilot users. If AD or Azure directory sync manages your users and groups then you need to create the pilot group in your source directory and add the test users first. Then, add that new group to your Duo directory sync configuration and perform a manual sync to import the pilot group to Duo.
- Create a new Trusted Endpoints policy with corresponding management integration configurations that enable detection and reporting of device management status.
- Apply the new policy to the pilot group on the test application and enable the management integration.
- Duo Premier and Duo Advantage plans: Monitor Device Insight and Endpoints in the Duo Admin Panel. Duo Essentials customers can monitor the Authentication Logs report to see when users authenticate from a trusted access device. As the pilot users authenticate their endpoints will start reporting their managed status to Duo.
- Expand the Duo Trusted Endpoints policy to all users and applications by adding it to the Global Policy.
- Start using the Trusted Endpoints policy to block access to your sensitive applications (optional).
Duo Management Integration Deployment
Before you can use the Trusted Endpoints policy for reporting or controlling access to applications, you'll need to perform some configuration steps in Duo and your device management system, and then distribute the Duo certificate, Duo Desktop, or Duo Mobile to your organization's managed devices. We've created guides for these deployment options:
- Duo Mobile app verification of mobile devices
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) verifies domain information obtained with Duo Desktop or with managed certificate enrollment using Group Policy and the Duo Certificate Proxy
- Workspace ONE managed device verification
- Cisco Secure Endpoint security posture verification
- Cisco Meraki Systems Manager managed device verification
- Generic Duo Desktop Integrations for other Windows and Mac OS endpoint management tools
- Google Workspace (formerly known as G Suite) managed device verification
- Chrome Device Trust Connector managed ChromeOS and Chrome browser verification
- Google Verified Access managed Chrome device verification
- Ivanti Endpoint Manager Mobile (formerly known as MobileIron Core) managed device verification
- Ivanti Neurons for MDM (formerly known as MobileIron Cloud) managed device verification
- Jamf Pro verifies domain information obtained with Duo Desktop or certificate policy deployment
- LANDesk Management Suite (Ivanti) certificate distribution package deployment
- Manual Enrollment with Duo Desktop
- Manual import of the Duo certificate to the local user's certificate store or keychain
- Microsoft Intune managed Android, iOS, and Windows device verification
- Sophos Mobile managed device verification
You can use any or all of these deployment options in your environment. In fact, we recommend configuring more than one to ensure that you enroll as many trusted endpoints as possible.
Applying the Trusted Endpoints Policy to Applications and Groups
Create a new policy with the Trusted Endpoints setting. At first, configure the policy to check for management status.
-
Log on to the Duo Admin Panel as an administrator with the Owner or Administrator admin role.
-
Navigate to the details page on the application you'll use to pilot the Trusted Endpoints policy.
-
Click the Apply a policy to groups of users link to assign the new Trusted Endpoints policy to just the pilot group.

-
Click the Or, create a new Policy link instead of selecting a policy to apply from the drop-down list.
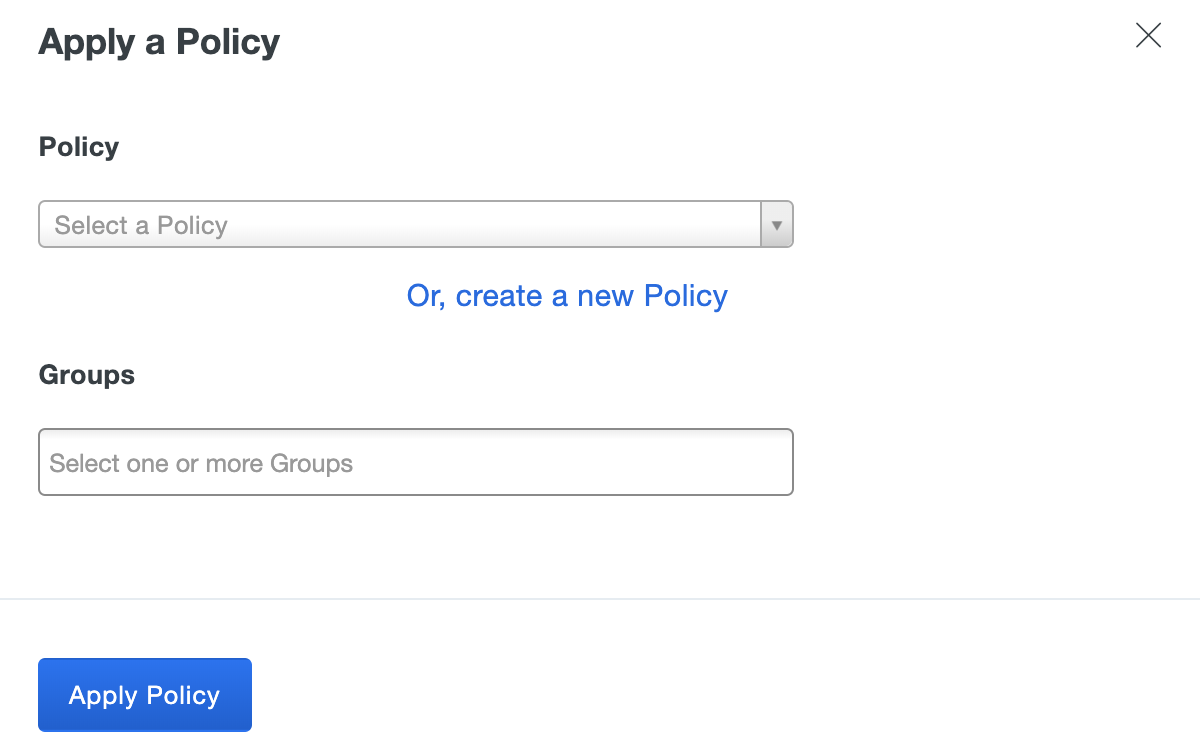
-
The policy editor launches with an empty policy.
-
Enter a descriptive Policy Name at the top of the left column, and then click the Trusted Endpoints policy item on the left. Change the selected option to Allow all endpoints.

-
Click the Create Policy button to save the settings and return to the "Apply a Policy" prompt, with the new Trusted Endpoints policy selected. Start typing in the pilot group's name in the Groups field and select it from the suggested names.
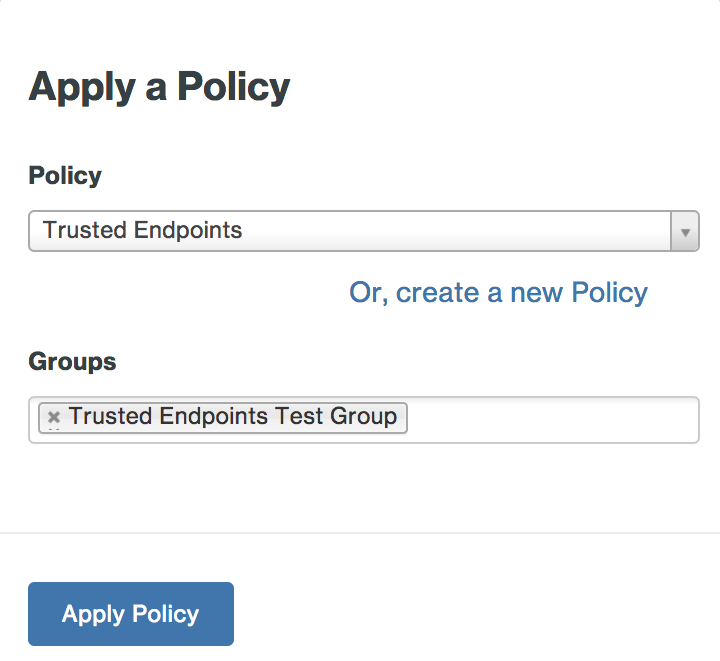
-
Click the Apply Policy button. The application page shows the new group policy assignment.
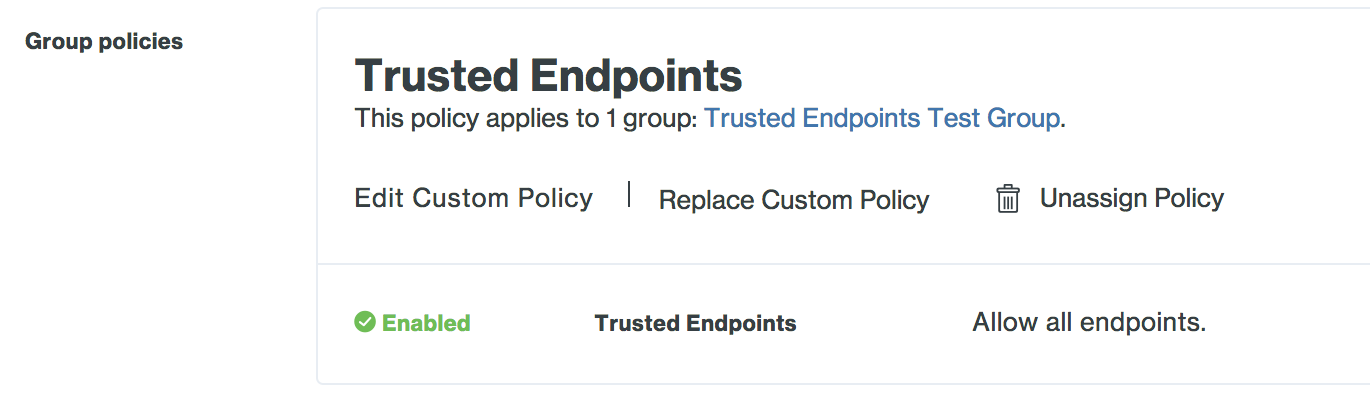
For more information about creating and applying group policies, see the Policy documentation.
Cisco Secure Endpoint
The Cisco Secure Endpoint integration verifies Windows and macOS endpoint status in Cisco Secure Endpoint and blocks access from Duo trusted endpoint client systems that Cisco Secure Endpoint identifies as "compromised". Learn more about Duo and Cisco Secure Endpoint.
Mobile Trusted Endpoints Policy
Your organization may want to apply different Duo trusted endpoint policies to computer endpoints and mobile devices. For instance, you may want to track the status of application access by unmanaged workstations without blocking access, while at the same time preventing application access from unmanaged mobile endpoints.
Accomplish this by clicking the Enable Advanced Options for Mobile Endpoints option within the Trusted Endpoints policy setting to expose the mobile-only selections. Once the mobile options for trusted endpoints have been enabled, Duo uses the accessing browser's user agent string to distinguish between mobile and traditional endpoints and apply the configured policy setting based on the endpoint's platform.

Since the user agent is self-reported by the browser, it's possible to manipulate the user agent string contents from the client side to make it appear as a different browser or operating system to Duo, with the potential effect of bypassing a trusted endpoints policy intended to block access.
Duo generally recommends using the default trusted endpoints policy settings for all types of endpoints to protect against policy bypass due to user agent spoofing.
Monitoring Trusted Endpoints
Plans Required to view Device Insight and Endpoints Pages: Duo Premier or Duo Advantage
As users access the application that has the Trusted Endpoints policy, they see no difference in the Duo Prompt when authenticating but Duo notes whether the devices used are managed or not. When you view these endpoints in the Admin Panel (from the Endpoints page, from the details page for that device, or from an individual user's details page), the "Trusted Endpoint" column shows the device certificate status: "Yes" if the endpoint passed Duo's managed system check, or "No" if it did not.
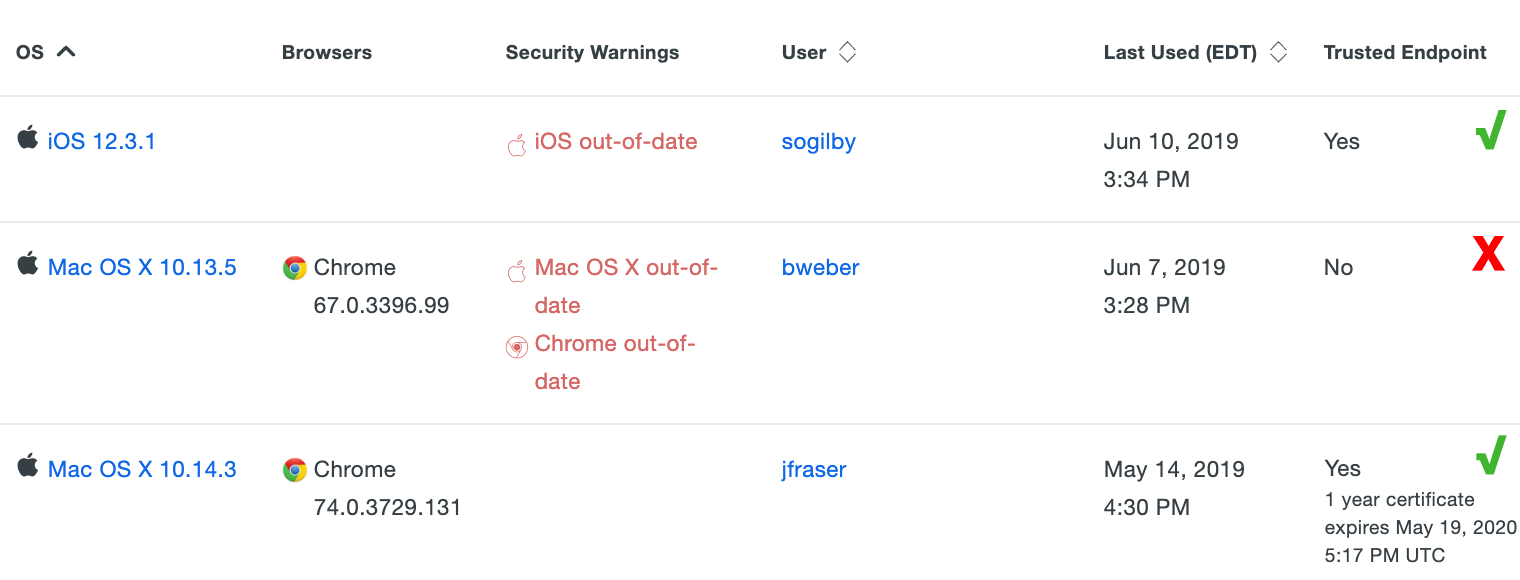
"Unknown" status in the Trusted Endpoint column usually indicates that the endpoint hasn't been used to access the application that has the Trusted Endpoints policy yet.
If Duo can determine the when the certificate was issued that information is shown along with the other information for that endpoint. When filtering the Endpoints table by certificate expiration, "soon" means that the certificate has reached its renewal window: three days before expiration for 1-week certificates or two weeks before expiration for one year certificates.
Expand the Trusted Endpoints Policy Scope
To include more of your users in the Trusted Endpoints pilot, return to the Duo Admin Panel and either add more users to the pilot Duo group or apply the test policy to additional groups from the test application's details page, You can also apply the Trusted Endpoints policy to additional applications.
Add even more users to your testing by switching from applying the Trusted Endpoints policy to specific groups on an application to applying the policy to all users of that application. Click the Apply a policy to all users link on an application's details page and select the Trusted Endpoints policy.

Eventually, you should add the Trusted Endpoints policy to your Duo Global Policy, so that all your browser-based application default to checking for the Duo device certificate.
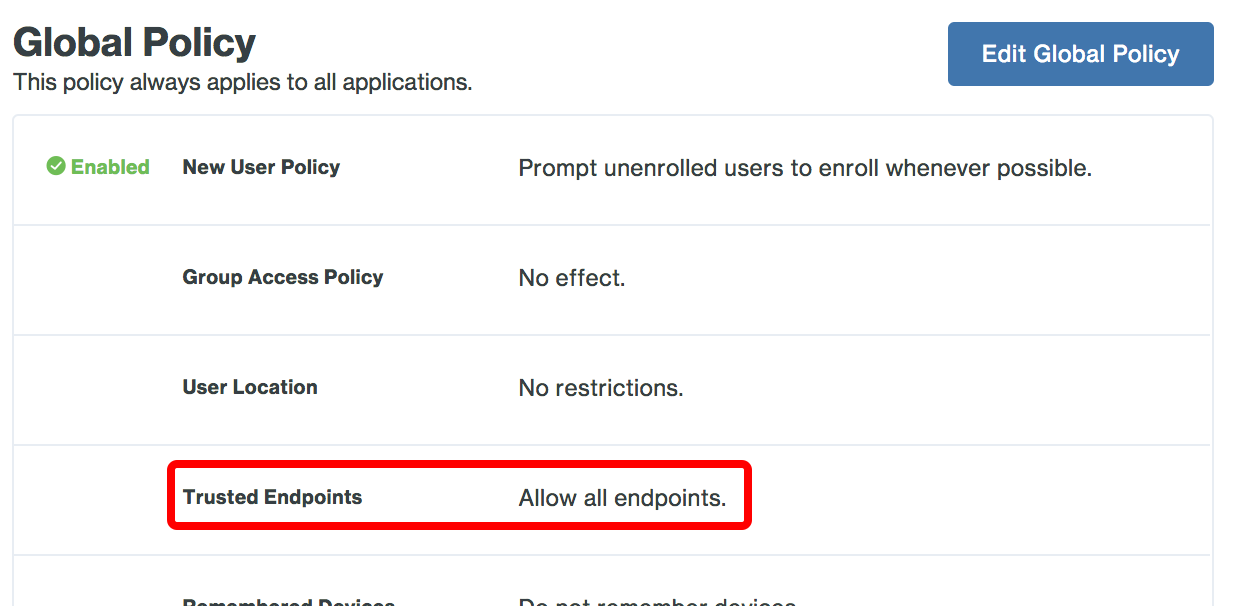
Control Application Access with the Trusted Endpoints Policy
When the majority of your devices have Duo Desktop installed or the Duo certificate present and report trusted status back to Duo, you may wish to block access to your more sensitive applications from unmanaged devices. Accomplish this by applying a policy with the "Trusted Endpoints" policy option set to Require endpoints to be trusted.
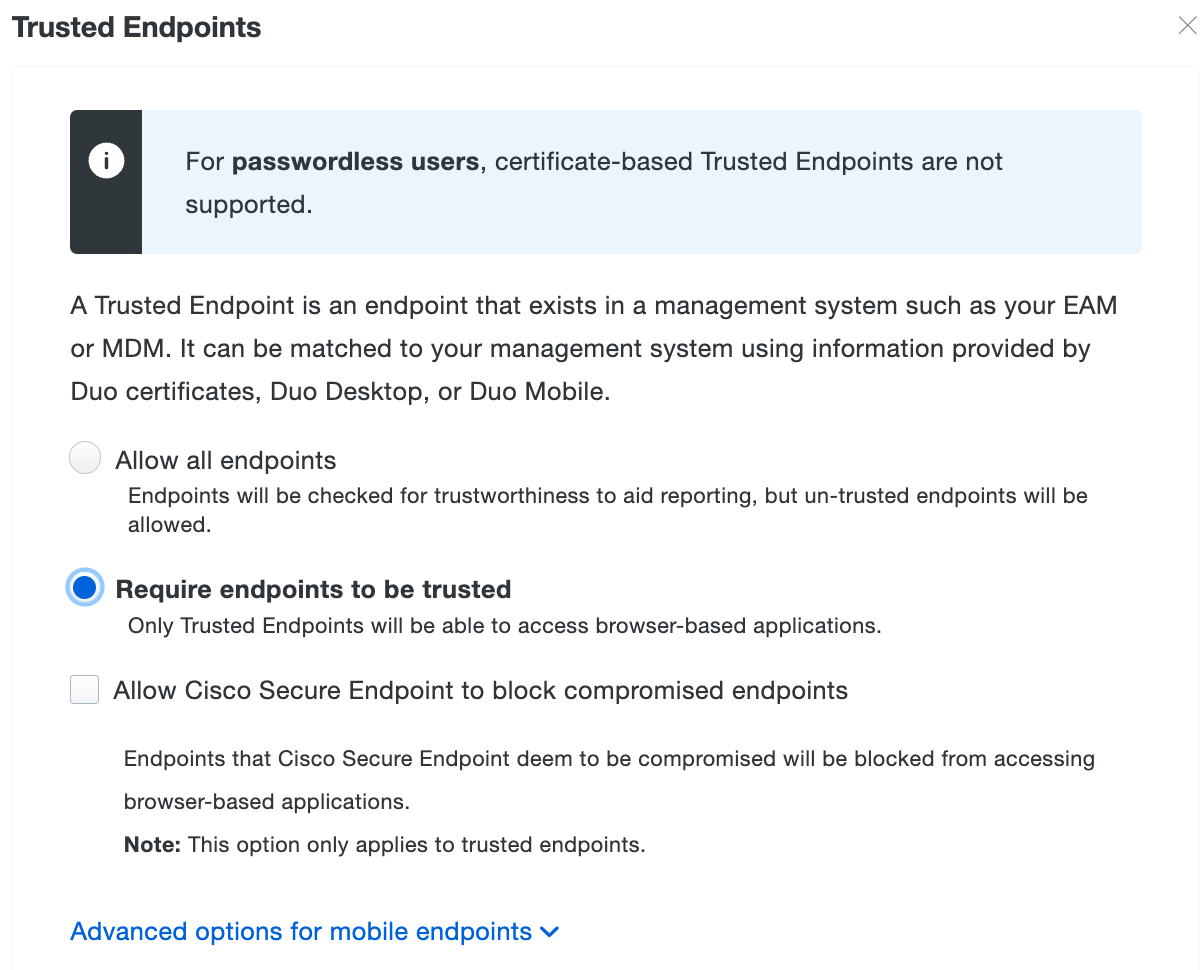
Users accessing the applications with this policy from trusted devices see no change in the Duo Prompt when authenticating. However, if the device does not pass the trusted device check then Duo prevents the user from authenticating.
Traditional Duo Prompt
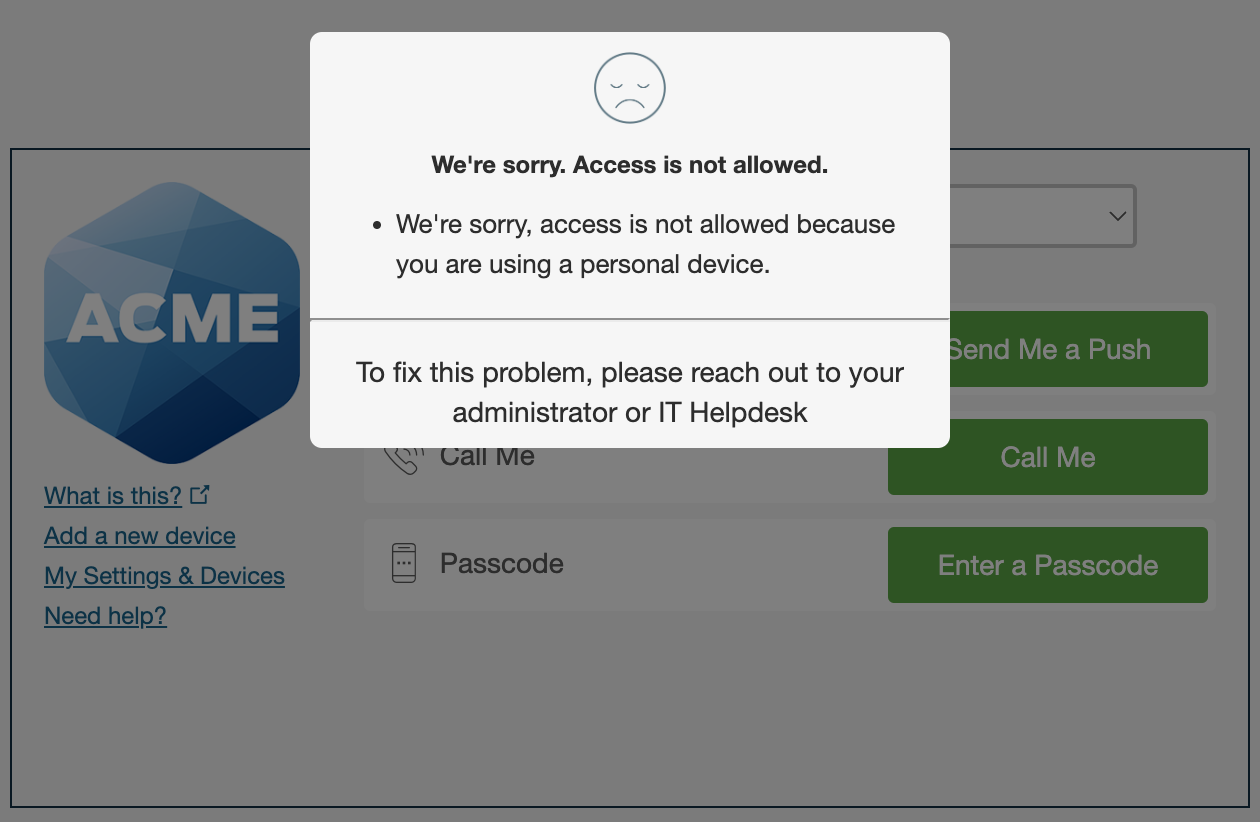
Duo Universal Prompt
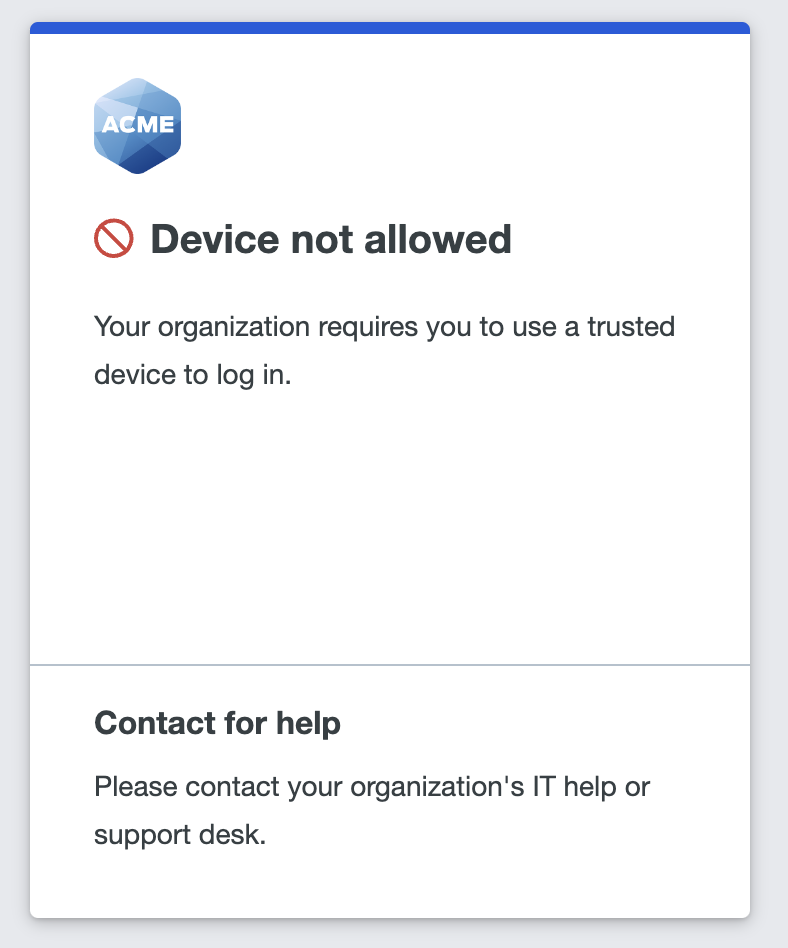
Don't enable this policy setting before deploying Duo Desktop or a Duo device certificate to your trusted access devices, or you may inadvertently block users' access to applications.
Deny Access to Endpoints
Plans Required: Duo Premier or Duo Advantage
You can deny trusted endpoints individually to prevent access to applications which have a Trusted Endpoint policy applied that blocks access from untrusted devices. Learn how to deny access to an individual endpoint.
Shared Device Authentication
Shared device authentication eliminates repetitive Duo Desktop authentication setup for users without individual workstations. When enabled, designated users perform interactive authentication enrollment with Duo Desktop once from a trusted endpoint. Subsequent Duo Desktop authentication enrollments from additional computers happen silently. See Shared Device Authentication for more information.
Deployment Setup Tips
Most organizations will want to test the Trusted Endpoints feature on a select group of users before deploying the feature to their entire user population. Below are instructions on how to achieve commonly desired configurations while avoiding user interruptions during your testing and deployment.
For each of the desired configurations documented below, once completed, the Endpoints menu can be used to filter users devices based on their trust status using the "Trusted Endpoint" filter.
We would like test with a pilot group of users and identify which of these users are accessing applications using trusted devices and which are not using trusted devices. We don’t want anyone to be blocked regardless of which type of device they are using.
-
Create a group in Duo or identify a synced directory group that contains the members of the pilot group.
-
To enable Trusted Endpoint identification for:
a. All applications: Make sure the global policy setting for Trusted Endpoints is set to Allow all endpoints. This is the default and cannot be changed unless at least one Trusted Endpoint Configuration exists. Identification of trusted endpoints will not start until an applicable Trusted Endpoint Configuration is enabled.
b. One application: Create an application or group custom policy for the desired application with the policy setting for Trusted Endpoints set to Allow all endpoints. This is the default and cannot be changed unless least one Trusted Endpoint Configuration exists. Identification of trusted endpoints will not start until an applicable Trusted Endpoint Configuration is enabled.
-
Create a Trusted Endpoint Configuration using your chosen management tools integration and configure it according to its instructions. A Trusted Endpoint Configuration will be created in the disabled state and thus will not have any effect on when trusted endpoint identification will be attempted.
-
On the Trusted Endpoints Configuration:
a. Locate the "Change Integration Status" section of the page, which shows the current integration status.
b. Toggle from the disabled state to the active state.
c. Select the Test with a group option and select the desired group from the drop-down menu.
d. Click Save.
-
Members of the pilot group will have their devices identified as trusted.
Note: Identifying trusted devices sometimes requires that users take extra actions during authentication, such as launching Duo Mobile on mobile devices. The advanced option Allow all mobile endpoints can be used to avoid extra authentication steps on mobile devices.
We would like to identify which users in a pilot group are accessing applications using trusted devices and which are not using trusted devices, and we would like to block access to anyone in the pilot group who is not using a trusted device.
To block access to applications from devices that are not trusted for only a pilot group of users, each application will have to be configured with the "Require endpoints to be trusted" Trusted Endpoints setting as described below.
-
Create a group in Duo or identify a synced directory group that contains the members of the pilot group.
-
Create a custom policy for the desired application with the policy setting for Trusted Endpoints set to "Require endpoints to be trusted."
-
Create a Trusted Endpoint Configuration using your chosen management tools integration and configure it according to its instructions. A Trusted Endpoint Configuration will be created in the disabled state and thus will not have any affect on when trusted endpoint identification will be attempted.
-
On the Trusted Endpoint Configuration:
a. Locate the "Change Integration Status" section of the page, which shows the current integration status.
b. Toggle from the disabled state to the active state.
c. Select the Test with a group option and select the desired group from the drop-down menu.
d. Click Save.
-
Select the desired application and in the "Group policies" section, assign the custom policy from step 2 to the Duo group identified in step 1.
-
Members of the pilot group will have their devices identified as trusted or not trusted, with application access granted or blocked accordingly.
We currently use Trusted Endpoints to identify trusted desktop devices. We would like a pilot group of mobile users to be required to use a trusted mobile device without affecting our other users.
-
Create a group in Duo or identify a synced directory group that contains the members of the pilot group.
-
Create an application or group custom policy for the desired application with the policy setting for Trusted Endpoints set to Allow all endpoints. Then click on "Advanced options for mobile endpoints" and select the Require mobile endpoints to be trusted option. Once the policy is saved, apply it to the group created in step 1.
-
Create an additional Trusted Endpoint Configuration for mobile clients using your chosen management tools integration and configure it according to its instructions. A Trusted Endpoint Configuration will be created in the disabled state and thus will not have any affect on when trusted endpoint identification will be attempted.
-
On the Trusted Endpoint Configuration:
a. Locate the "Change Integration Status" section of the page, which shows the current integration status.
b. Toggle from the disabled state to the active state.
c. Select the Test with a group option and select the desired group from the drop-down menu.
d. Click Save.
-
Members of the pilot group will be required to use trusted mobile devices for that application.
We currently use Trusted Endpoints to require trusted desktop devices. We would like a pilot group of mobile users to be required to use a trusted mobile device without affecting our other users.
-
Create a group in Duo or identify a synced directory group that contains the members of the pilot group.
-
In the "Applications" menu, select the application you want to protect. Create a new group policy and set Trusted Endpoints to "Require endpoints to be trusted." Once the policy is saved, apply it to the group created in step 1.
-
Create a Trusted Endpoint Configuration of the desired type and configure it according to its instructions.
-
On the Trusted Endpoint Configuration:
a. Locate the "Change Integration Status" section of the page, which shows the current integration status.
b. Toggle from the disabled state to the active state.
c. Select the "Test with a group" option and select the group from step 1 in the drop-down menu.
d. Click "Save" and the members of the pilot group will be required to use trusted desktop AND mobile devices for that application.
I am already using the test mode successfully and I want to add more users to the test.
Simply add additional users to the pilot group that was created to test the trusted endpoints feature.
I am already using the test mode successfully and I want to add more applications to the test.
In each application that you want to test, in the "Group policies" section apply the already created custom policy to the Duo group you created previously.
I am satisfied with testing and want to deploy to all users.
For each Trusted Endpoint Configuration that has been restricted to the pilot group, change its integration status to "Activate for all". Then for each application that has a custom group policy, either replace the group policy with an "Application policy", or delete the group policy so that the global policy is enforced.
Troubleshooting
Need some help? Take a look at our Trusted Endpoints Knowledge Base articles or Community discussions. For further assistance, contact Support.
Note: Browser extensions such as Privacy Badger and Ghostery can interfere with Duo's certificate collection and cause Trusted Endpoints to not work as expected for end users.
All Duo customers have access to Level Up, our online learning platform offering courses on a variety of Duo administration topics. To access Level Up content, sign in with the same email address you use to sign in to the Duo Admin Panel.
Level Up course: Enforcing Trust-Based Access with Duo Policies
